Free downloadable software shows the characteristics of the current-mode buck-boost (flyback) converter.
Introduction
In this article, Dr. Ridley presents a summary of the buck-boost converter with voltage-mode control. Free analysis software—the fifth in a series of six—is provided to readers of this column to aid with the analysis of their voltage-mode buck-boost converters.
Voltage-Mode Buck-Boost Converter
In the early days of power electronics, there were three basic topologies: the buck, the boost, and the buck-boost. Variations of these three topologies solved most power conversion problems, and continue to do so today.
In the last 4 articles, the buck and boost converter control characteristics have been presented, using voltage-mode or current-mode control. The final two articles of this series present the buck-boost converter (or, in its isolated version, the flyback converter.) Like the boost converter, the buck-boost can be a challenging converter to stabilize.
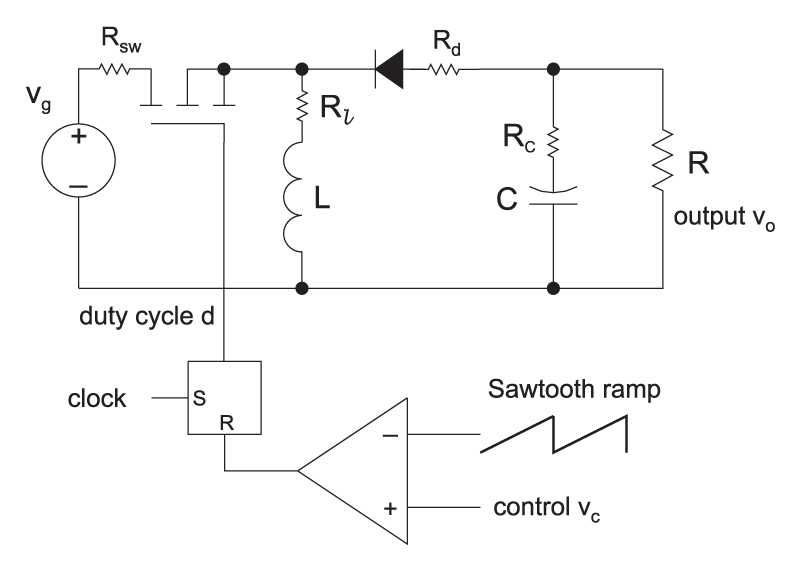
Figure 1 shows the standard buck-boost converter operating with voltage-mode control.
Figure 1: Buck-Boost converter with voltage-mode control.
For the buck-boost converter of Figure 1, the equation for the control-to-output transfer function is:
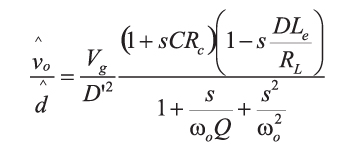
Where the resonant frequency is given by
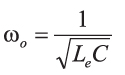
And the equivalent inductance is determined by the duty cycle:
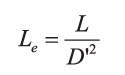
The Q of the filter is a complex combination of the parasitic resistances shown in the circuit and the load resistance. For this equation, you can refer to either [3] or [5].
Buck-Boost Converter Right-Half-Plane Zero
Like the boost converter, the buck-boost converter has a right-half-plane (RHP) zero, as seen in the transfer function above. As with the boost, when the buck-boost converter switch is turned on for a longer period of time, the inductor is disconnected from the load for a longer period of time. That means that the output initially drops, even though the control command is trying to make it increase. This is the classic characteristic of a RHP zero.
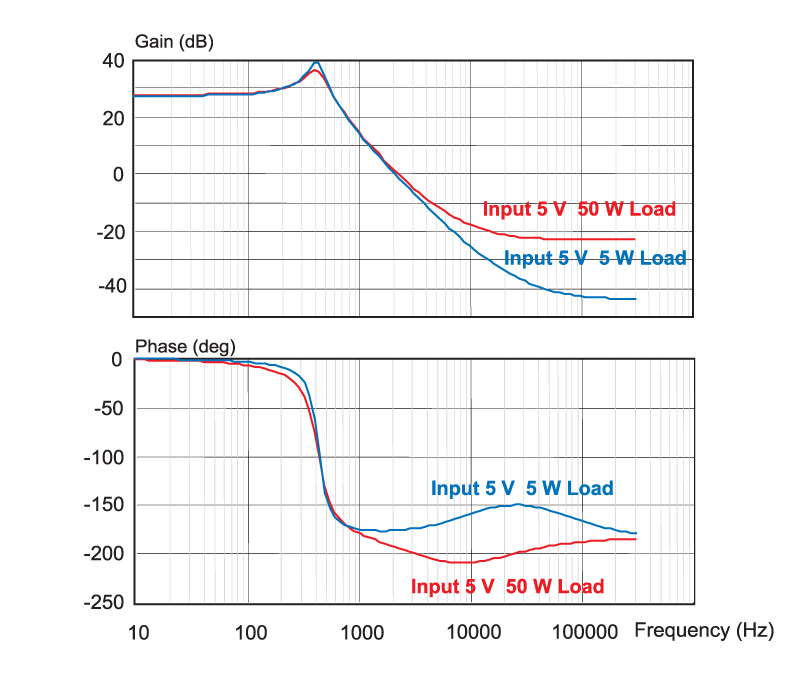
Figure 2 shows the effect on the gain and phase of the RHP zero. At heavy loads, the RHP zero frequency is the lowest, and the phase delay is the greatest. At light loads, the RHP zero frequency is higher, and the converter is easier to control.
Figure 2: Effect of changing loads on the control characteristic of the buck-boost converter.
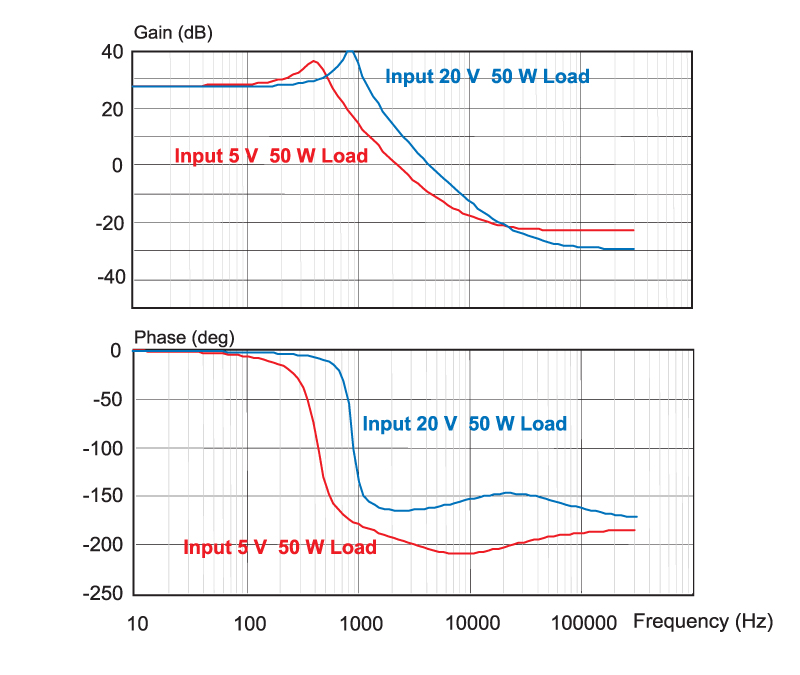
The operation of the buck-boost converter also causes a shift in the resonant frequency with input voltage, as can be seen from the control equations. Figure 3 shows how the characteristics of the buck-boost converter varies significantly with a wide input voltage.
Figure 3: Effect of input line variation on the control characteristic of the buck-boost converter.
For converters with RHP zeros, design is usually done at the lowest input line and the maximum load. This condition has the lowest value of RHP zero, and the lowest value of resonant frequency. The moving resonant frequency can create problems at different operating points, and the whole range of operation should be carefully checked with both prediction and measurements.
More equations are created when the buck-boost converter operates in discontinuous-conduction mode (DCM). The free software provided for the boost converter will automatically assess which mode of operation your converter is in, and provide the proper transfer function.
Important Characteristics
There are several important points to remember about the buck-boost converter operating in continuous-conduction mode:
There is a double pole at the resonant frequency of the LC filter. The frequency of this double pole will move with the operating point of the converter since it is determined by the equivalent inductance of the circuit, and this is a function of duty cycle. At low line, the resonant frequency has its lowest value.
There is a zero in the control-to-output transfer function corresponding to the ESR of the output filter capacitor.
The buck-boost converter has a right-half-plane zero which can make control very difficult. This RHP zero is a function of the inductor (smaller is better) and the load resistance (light load is better than heavy load). The bandwidth of the control feedback loop is restricted to about 1/5th the RHP zero frequency.
In discontinuous conduction mode, the resonant frequency of the filter is eliminated from the control characteristic, as predicted by the switch model in [5]. This simplifies the control loop design, but higher power boost converters are usually designed to operate in CCM for efficiency reasons.
Most buck-boost (or flyback) converters are low power – 10 W or less. And most of them are designed to operate only in discontinuous conduction mode. This makes the control much simpler, but it is often very difficult to avoid going into CCM under all conditions. As power levels rise, trying to keep the converter in only DCM puts excessive stress on the power switch. As we will see with the next article, current-mode control makes the RHP zero issue much more manageable.
Buck-Boost Converter Voltage-Mode Software
Software is available for download that allows you to predict the small-signal response of your buck-boost converter with voltage-mode control. After entering your power stage values and switching frequency, the transfer function gain and phase of the power stage is plotted for you, and the resulting poles and zeros given.
The software is designed to run under either Excel 2007 or Excel 2003. Make sure when you open the software that the macro features are enabled in order to use the program properly. Please go to http://www.ridleyengineering.com/freesoftware.htm to download the software.
Summary
The buck-boost converter is very widely used in industry, in the format of the isolated flyback. It is a very useful topology, but care and time must be taken to properly design the control loop, especially when operating in CCM. The inductor should be chosen carefully for a controllable power stage RHP zero characteristic. It is not necessary to run the converter always in DCM, but this may be the preferred mode of operation for low-power converters. As with all converters, measurement [2] is essential to ensure a stable and rugged product.
References
- Join our LinkedIn group titled “Power Supply Design Center”. Noncommercial site with over 7000 helpful members with lots of theoretical and practical experience.
- For power supply hands-on training, please sign up for our workshops.
- “A New Small-signal Model for Current-Mode Control”, Raymond B. Ridley,1990 PhD dissertation, free download is available.
- “Measuring Frequency Response, Tips and Methods”
- “Switch-Mode Power Supplies”, Christophe P. Basso, published by McGraw-Hill, 2008.
- Power 4-5-6 Design Software
- “Fast Analytical Techniques for Electrical & Electronic Circuits”, Vatché Vorpérian, published by Cambridge University Press, 2002.